Thyroid disease and hair loss - what's behind it?
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the neck - but its effect on the entire body is enormous. It controls metabolism, hormone production and cell regeneration. If it gets out of balance, this affects many areas - including hair health.
Many people affected by thyroid disorders not only notice tiredness, weight fluctuations or mood swings, but also increased hair loss. But what exactly is the reason for this?
Hair loss and thyroid disease: an overview of the causes
Hormonal imbalances and hair loss
The thyroid gland plays a central role in metabolism. It produces the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which affect almost all cells in the body - including the hair follicles. If hormone production is out of balance, this can lead to disruptions in the hair cycle.
Influence on the hair roots
Both hypofunction and hyperfunction have a negative effect on the hair roots:
- If there is an undersupply, the cell metabolism slows down, the hair grows more slowly and falls out more easily.
- Overproduction puts the hair roots under constant stress, which can also lead to diffuse hair loss.
Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid)
In the case of hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland produces too few hormones. This causes the metabolism to run at a low level. The result: hair grows more slowly, becomes finer and falls out more frequently. This is often accompanied by a dry, sensitive scalp.
Typical signs of hypothyroidism:
- Sensitivity to cold
- Weight gain
- Listlessness and tiredness
Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland)
In the case of hyperfunction, the metabolism works at full speed. Although the hair grows faster at first, the hair follicles lose their rhythm due to the permanent state of stress. The result is diffuse hair loss, which can occur evenly across the entire head.
Typical signs of hyperthyroidism:
- Nervousness and inner restlessness
- Weight loss despite a normal diet
- Excessive sweating
Note: Anyone who notices signs of a thyroid disorder should consider a medical examination (including a blood test of thyroid levels). An appropriate therapy can not only alleviate metabolic problems, but also stabilize hair growth.
Autoimmune diseases as triggers
Autoimmune diseases can also play an important role in hair loss. Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease are particularly well known in this regard. Both diseases affect the thyroid gland and cause the immune system to mistakenly attack the body's own tissue.
This permanent incorrect reaction leads to inflammatory processes that put a strain on the thyroid gland and increasingly impair its function. This results in fluctuations in the hormone balance, which have a direct effect on hair metabolism.
Why autoimmune diseases affect the hair
- Chronic inflammation of the thyroid gland weakens the entire metabolism.
- Irregular hormone levels (e.g. hyper- or hypofunction) throw the hair cycle out of balance.
- The hair metabolism is put under additional strain, which increases the risk of diffuse or increased hair loss.
Note: If an autoimmune disease is suspected, it is essential to seek medical advice. Targeted treatment of the thyroid gland can not only improve general well-being, but also significantly reduce hair loss.
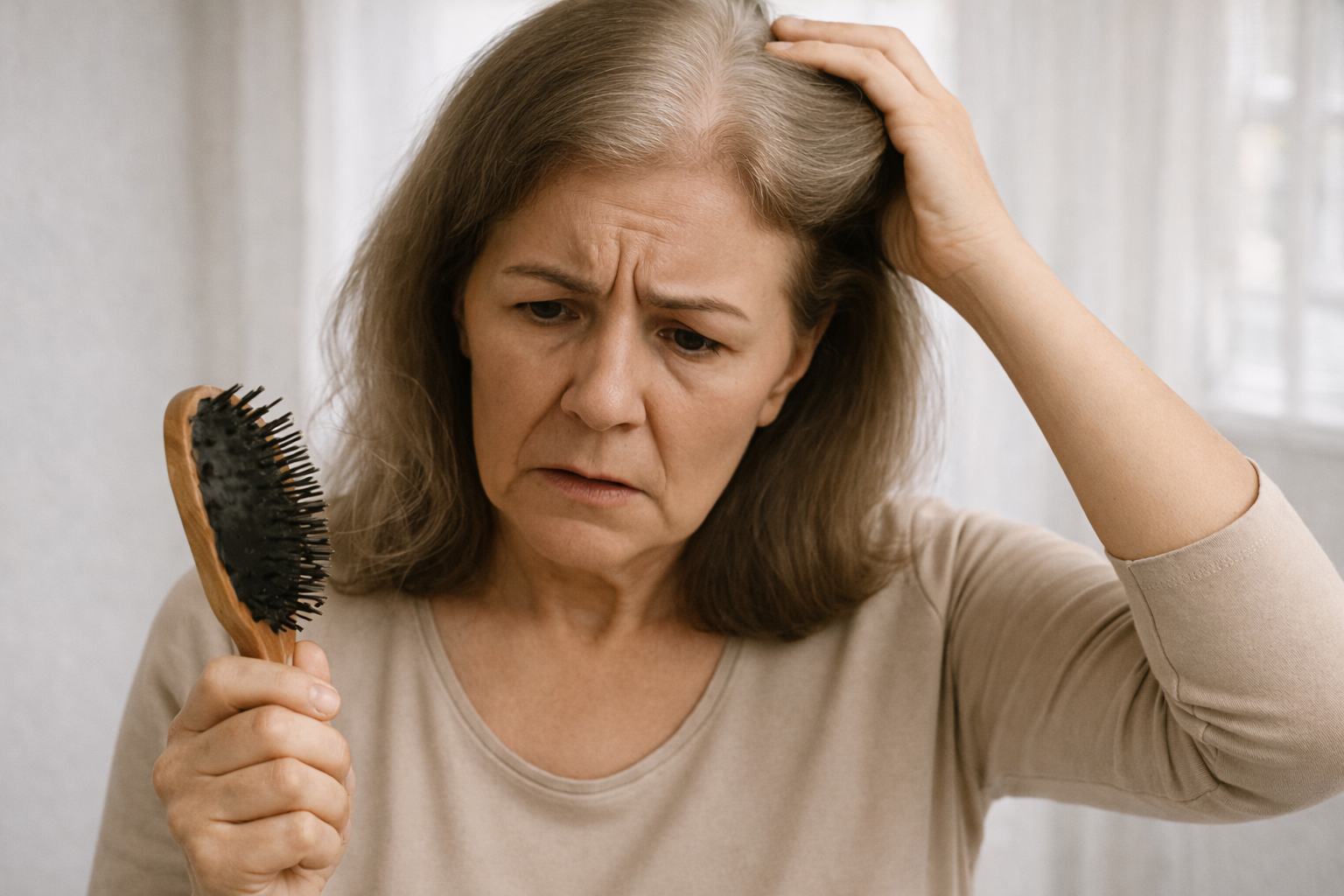

Diagnosis: How to recognize hair loss due to thyroid disease?
Typical symptoms besides hair loss
- Tiredness or nervousness
- Weight gain or sudden weight loss
- Sensitivity to cold or heat
- Brittle nails and dry skin
When to see a doctor?
If hair loss suddenly increases sharply or other symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness or severe exhaustion occur, it is essential to seek medical advice.
Blood test as the gold standard
An endocrinologist or GP can determine the hormone status by means of a blood test. Important values are
- TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
- T3 and fT4
- Antibody values if autoimmune diseases are suspected
Supplementary diagnostics
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
- Physical examination
- Medical history of diet and lifestyle
What helps with hair loss due to thyroid disease?
Medical therapy
- Hypofunction: treatment usually with L-thyroxine
- Hyperfunction: medication to inhibit hormone production
- Autoimmune diseases: individual therapy after medical clarification
Patience is important
The hair reacts with a delay - it usually takes several months for the situation to improve after the start of therapy.
Nutrition & micronutrients
A nutrient-rich diet supports the hair follicles:
- Iodine (e.g. from algae or iodized salt)
- Selenium (e.g. from Brazil nuts)
- Iron & zinc for cell regeneration
- Vitamin D as an important co-factor
Nutrition tip for hair loss due to thyroid disease
A food diary can help to make connections between symptoms and food visible.
Scalp care & hair serums
In addition to medical therapy, nourishing hair serums with natural active ingredients can soothe the scalp and strengthen the hair roots. They are not a substitute for therapy, but have a supportive effect to revitalize the hair follicles.
Suitable ingredients
- Caffeine to stimulate blood circulation
- Rosemary extract has an antioxidant effect, promotes blood circulation and regeneration
- Biotin for cell health
- Plant extracts to soothe the scalp
In conclusion: Take a holistic approach to hair loss caused by thyroid disease
Impaired thyroid function or thyroid disease can have a significant impact on hair growth. Anyone suffering from persistent hair loss should therefore definitely have their thyroid checked by a doctor.
In addition to medical treatment, targeted care of the scalp can be beneficial. Products such as Laduti Hair Growth Serum rely on natural ingredients such as biotin, caffeine, plant extracts and vitamins, which supply the hair roots with nutrients and soothe the scalp. This optimally supports the hair during phases of hormonal fluctuations – as a supplement, but not a replacement for medical therapy.

FAQ
Can hair loss be the first sign of thyroid disease?
Yes, hair loss is often one of the first visible symptoms - especially in the case of diffuse thinning over the entire head.
Does hair grow back after thyroid treatment?
In many cases, the hair cycle stabilizes again after a few months. Consistent medical treatment and patience are important.
Which vitamins help with hair loss due to thyroid disease?
Biotin, zinc, selenium and iron are particularly relevant. These micronutrients support the metabolism and regeneration of the hair roots.
Can a hair restorer treat a thyroid condition?
No, a hair restorer does not replace medical therapy. However, it can care for the scalp and strengthen the hair follicles in a targeted manner so that the hair is better nourished.
Can Laduti help with thyroid-related hair loss?
Yes, Laduti Hair Serum combines natural active ingredients such as caffeine, plant extracts, and the innovative complexes AnaGain™ and Procapil™, which strengthen the hair roots and nourish the scalp – a supportive addition to medical treatment.

